About Urea Fertilizer
Urea is nitrogen fertilizer with an NPK (nitrogen-phosphorus-potassium) ratio of 46-0-0. The chemical formula of the urea is close in composition to the organic formulation of the urea, which also provides a number of advantages in the mass use for feeding crops. Although urea is naturally produced in humans and animals, synthetic urea is manufactured with anhydrous ammonia.

History
Urea was discovered in 1773 by the French chemist Hilaire Rouelle. In 1828, German chemist Friedrich was obtained by reacting silver isocyanate with ammonium chloride. This was the first time an organic compound was obtained artificially from an organic compound.

what is Urea Fertilizer?
Another name of this fertilizer is (Carbamide) is an organic compound with the NH2COONH4 chemical formula, and is used as one of the most consumable and, of course, the cheapest chemical fertilizers that supply N to the rest of the world.
Urea is neither acidic nor alkaline, highly water-soluble and relatively non-toxic, and urea is widely used in chemical fertilizers as a rich and suitable source of nitrogen. Urea is also one of the most important raw materials in the chemical industry.
Urea is hydrolyzed in the soil and converted to ammonia and dioxide. The solubility of urea is very high in water, which is used for fertilizer and spray application on the plant. 46% of urea is composed of nitrogen.
Urea is nitrogen fertilizer with an NPK (nitrogen-phosphorus-potassium) ratio of 46-0-0. The chemical formula of the urea is close in composition to the organic formulation of the urea, which also provides a number of advantages in the mass use for feeding crops. Although urea is naturally produced in humans and animals, synthetic urea is manufactured with anhydrous ammonia.
Other names of urea fertilizer: Amide of carbonic acid, carbamide, carbamide acid, carbonyl diamide, carbonyl diamide, carbonyl diamine, isaurea.

Safety information
Urea causes skin and eye irritation and has respiratory complications. Continuous exposure to the skin causes swelling in the skin. Its high concentration in the blood causes damage to the organs of the body. Heat it above the melting point causes it to decompose and generates toxic vapors. Normally not flammable, but its mixing with strong oxidants such as nitride causes explosion.

Urea storage
Urea absorbs moisture from the atmosphere and the surface of the air, it is typically used to store it. Also, if you need to store it in bulk, it should be covered with a special cover and water insulator. It is also recommended that urea be stored, as well as many other solid fertilizers, in a cool and dry place, where the ventilation is well done.

Nitrogen fertilizer
Nitrogen (Nitrogen) is one of the most important nutrient requirements for plants and common types of chemical fertilizers .Farmers use N fertilizers to accelerate the growth and increase the yield of their agricultural products. The main common types of nitrogen fertilizers are urea fertilizer, ammonium nitrate, ammonium sulfate. Nitrogen can be found in many different forms and from a number of sources as listed in Table. Among these sources urea tends to be the dominant nitrogen fertilizer used in agriculture.
| Forms of nitrogen | Source |
| Organic nitrogen | Animal manure, compostand plant residues |
| Urea | Commercial fertilizerand fresh manure |
| Ammonium (NH4+) | Chemical fertilizers such as ammonium nitrate and ammonium sulfate, fresh manureand breakdown of organic matter into the soil |
| Nitrate (NO3-) | Chemical fertilizer such as ammonium nitrate and potassium nitrate |
| Nitrogen gas (N2) | About 80% of air within soil spaces |
(Forms of nitrogen and their potential sources)

Urea fertilizer production method
In the industry, urea is produced from carbon dioxide and ammonia. Usually, a large amount of carbon dioxide is produced during the process of producing ammonia from coal, natural gas, or oil. This causes direct urea from the combination of these materials. The basis for the production of urea was made in 1922 under the name of the Urea Process by Bosch-Meiser. There are various processes for the production of urea in different conditions, all of which have more production losses than the process.
This process involves two major equilibrium reactions:
_ No reaction of dry ammonia liquid with dry ice
_The second reaction is the conversion of ammonia carbamide to urea in water.
Unreactive materials are used to produce other materials, including ammonium nitrate or ammonium sulfate

Tradeinfact Groupe
The most important factors affecting the success of Nitrogen fertilizers are prices, analyzes, packaging and the procedure of selling urea fertilizer which we will surprise you in all cases.many countries have sent orders to this group, especially from Asia, Europe and Africa. We have also responded to their answers.

Different types of Urea fertilizers
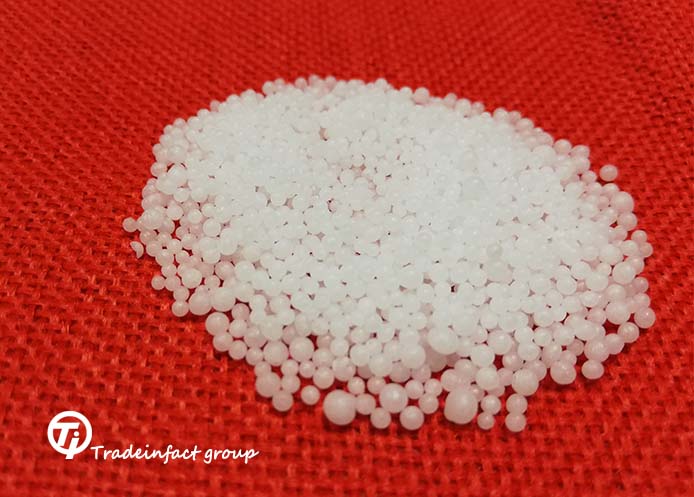
Urea fertilizer in terms of its shape is divided into two groups of granules and peril. Usually, both samples have the same analysis and 46% nitrogen. But they are different in terms of size, size and hardness

Difference in Urea Granule and Prill
Compared to the granular and urea fertilizer, we must say that N content of both is in the same range. Prill fertilizer is usually softer than granola. Usually the size of pearl is between 1 up to 2/4 mm but Granule is between 2 up to 4 mm. Some farmers prefer granules because they are gradually absorbed, and others think prill is better for faster absorption. It may seem strange, but based on the experience of Tradeinfact group, sometimes these two kinds of psychological aspects are chosen, and in some areas they prefer one to another.
Tradeinfact in Urea Fertilizer market
Tradeinfact Group has the ability to supply urea fertilizer in the shortest time and with the best price from petrochemicals.The global population growth over the past four decades has caused rapid growth of agricultural activities which in turn has increased the demand of fertilizer worldwide. In particular nitrogen fertilizers are the most common types used in the world of agriculture. Urea(46%) in the forms of prill and granule is one of our major activities. Among these sources urea tends to be the dominant nitrogen fertilizer used in agriculture.
If you have any questions, doubts or requests, please contact us.

Uses and Applications of Urea
Aside from its common use as fertilizer, there are other more ways of describing what is urea.Urea is an industrial product that is used as feed additive for livestock.It is an industrial product used in the manufacture of synthetic resins with various applications such as plastics, adhesives, moldings, laminates, plywood, particleboard, textiles, and coatings .Urea is an industrial product used in the production of pharmaceutical products. Other minor uses are as rehydrating lotion, diuretics, deicers, and cold-compresses.

Recommended urea usage fertilizer
The amount of urea uses depends on the type of product, soil analysis and environmental conditions. Therefore, it is advisable to determine the dosage based on the opinion of the agricultural expert. As the use of low fertilizer causes problems in agriculture, excessive use will also cause damage. The use of this type of fertilizer should be highly precise because it can cause changes in the pattern of plant growth or sometimes negative effects on plants due to high amounts of materials.
Recommended urea usage fertilizer
| PLANT TYPE | UREA (Kg/ha) |
| Rice plant | 250 |
| Hybrid Corn | 300-350 |
| Soybean | 100-150 |
| Peanut | 100-150 |
| Cassava/Yam | 200-300 |
| Red Onion/Garlic | 300-400 |
| Potato | 400-500 |
| Cabbage | 300-400 |
| Tomato/Chilli | 300-400 |
| Carrot | 300-400 |
| Long Bean/Bean | 100-150 |
| Broccoli/Cauliflower | 200-300 |
| Watermelon/Melon | 300-400 |
| Orange, Apple, Grape, Mango | 500-600 |
Reasons to get out N from the plant
- Vaporize
- Leaching
- Unsuitable time and method

Urea consumption in agriculture
More than 90% of the world’s urea production is for use as nitrogen-containing fertilizers.
_ Urea is used directly as a fertilizer in solid state and in granular and peril models in agriculture.
_ Urea is used as an additive in the production of chemical fertilizers such as NPK
_ Urea is used in the production of nitrogen fertilizer called UAN
_ Urea is used in some formulations of animal feed and poultry in a very low amount
Urea fertilizer application in agriculture
_ Spray application
_ Soil fertilization in solid form
_ Along with irrigation water

The Role of Nitrogen Fertilizers
- It accelerates plant growth by increasing cross-growth and longitudinal growth.
- Increasing the size and number of leaves and number of semiclusters in each cluster and increasing the percentage of semiclusters in each cluster and grain weight and length.

Symptoms of nitrogen deficiency
- Reduced Growth and Crop Performance: The first sign of nitrogen deficiency in the plant is reduced vegetative growth. Nitrogen is the most important element for plant growth, and its deficiency leads to reduced vegetative growth and, consequently, reduced yield.
- Leaves are yellow: N-deficiency usually leaves the old yellow leaves, while young leaves of the green plant remain. Therefore, the garden or farm becomes yellowish. Changes in the color of the leaves, veins and petioles to pale green or yellow will also result in a shortage. Symptoms of deficiency mainly occur in old leaves
- Minority of fruits and the loss of flowers and fruits: The small and small fruits and the excessive loss of flowers and fruits are other signs of nitrogen deficiency.
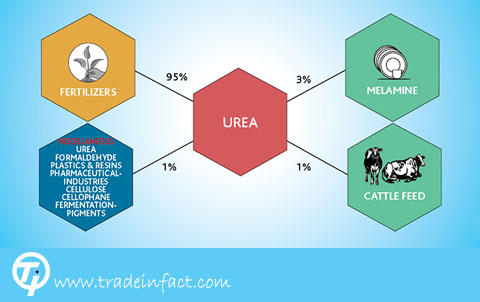
Industrial consumption
_ Types of plastics, in particular urea formaldehyde resins.
_ Types of adhesives, such as urea formaldehyde and urea melamine formaldehyde
_ Pharmaceutical and cosmetic industries
_ Preparation of fire powder
_ Potassium cyanide, as the starting material of some industries.
_ Nitrate urea, an explosive type.
_ Filter



